Understanding Chest Infection Complications and Their Impact on Health
Chest diseases are common respiratory ailments that affect millions of people every year. These infections range from mild conditions like bronchitis to more severe forms such as pneumonia, which can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly. The impact of chest diseases on human health is significant, and their complications can affect various parts of the respiratory system, cardiovascular health, and overall wellbeing. Understanding these complications is essential for both prevention and effective management.
What is a Chest Infection?
A chest infection refers to an infection that affects the airways or lungs, causing inflammation and making it difficult to breathe. It is commonly caused by viruses or bacteria. The two most common types of chest infections are:
- Bronchitis – An infection of the bronchial tubes (airways) that causes inflammation and increased mucus production.
- Pneumonia – An infection of the lungs themselves, where the air sacs become inflamed and filled with fluid or pus.
Chest infections can occur at any age, but individuals with weakened immune systems, the elderly, children, and those with pre-existing respiratory conditions like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are at a higher risk.
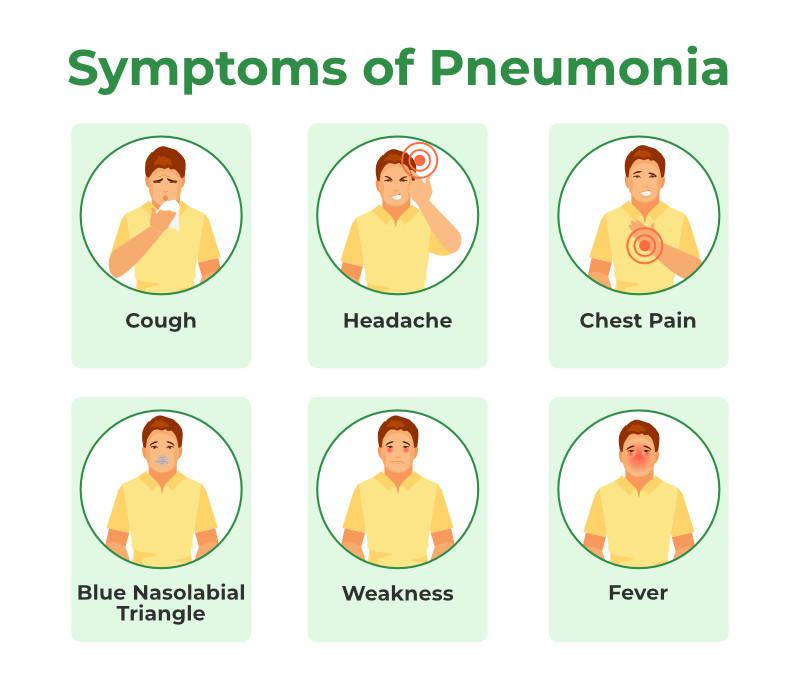
Common Symptoms of Chest Infections
The symptoms of chest infections can vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. However, common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Mucus production (which may be green or yellow)
While mild chest infections can often be managed at home with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications, more severe cases require medical attention. Complications arise when the infection is left untreated or when the immune system cannot cope with the severity of the infection.
Chest Infection Complications and Their Impact on Health
While chest infections are often treatable, they can lead to several complications, especially when left untreated or improperly managed. These complications can affect the lungs, heart, and overall health. Some of the most common complications include:
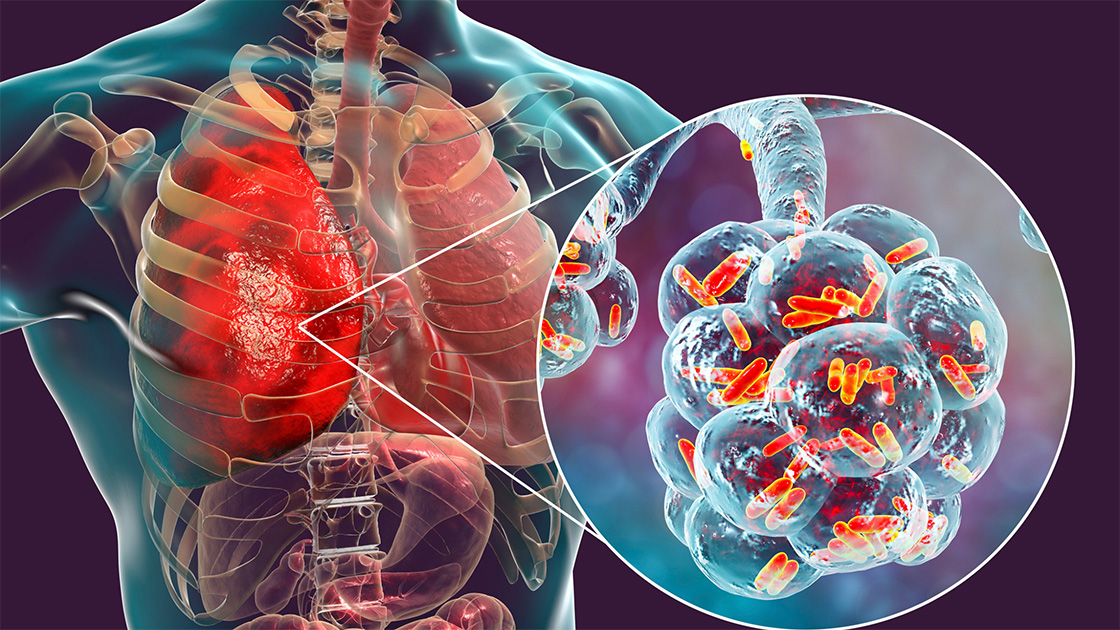
1. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is one of the most severe complications of a chest infection. It occurs when the infection spreads to the lungs and causes inflammation of the air sacs (alveoli). This results in fluid or pus accumulation, making it difficult for oxygen to enter the bloodstream. Pneumonia can be caused by both viral and bacterial infections.
Impact on Health:
- Respiratory Distress: The inflammation and fluid accumulation in the lungs make breathing difficult. This leads to shortness of breath, rapid breathing, and decreased oxygen levels in the body.
- Sepsis Risk: If pneumonia is left untreated, it can lead to sepsis, a dangerous infection that spreads throughout the body, causing widespread inflammation and organ failure.
- Long-Term Effects: In some cases, pneumonia can result in lasting lung damage, including scarring, decreased lung function, and an increased risk of developing chronic respiratory diseases.
2. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a severe form of lung injury that can occur as a result of a chest infection, especially pneumonia. It involves widespread inflammation of the lung tissue, causing the lungs to fill with fluid. This fluid accumulation disrupts the lungs' ability to exchange oxygen, leading to respiratory failure.
Impact on Health:
- Severe Breathing Problems: ARDS can cause extreme difficulty breathing, requiring mechanical ventilation (a ventilator) to support the patient’s breathing.
- Organ Failure: ARDS can cause a drop in blood oxygen levels, which might affect other organs, including the kidneys and heart, leading to organ failure.
- Long Recovery: People who survive ARDS may face prolonged periods of recovery, often requiring rehabilitation and lung therapy to regain normal lung function.
3. Pleural Effusion
Pleural effusion occurs when fluid builds up between the layers of the pleura, the membranes surrounding the lungs. This condition can occur as a complication of pneumonia or other chest infections. The accumulated fluid puts pressure on the lungs, making it difficult to breathe.
Impact on Health:
- Breathing Difficulties: The pressure exerted by the fluid on the lungs can cause difficulty breathing and chest pain.
- Infection Risk: In some cases, pleural effusion can become infected, leading to further complications such as empyema (pus-filled fluid in the pleural space).
- Treatment Needs: Treatment often involves draining the fluid through a procedure called thoracentesis. In severe cases, surgery may be needed to remove the fluid.
4. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Exacerbation
Chest infections, particularly viral infections like the flu, can trigger exacerbations in individuals with chronic respiratory conditions such as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). COPD is a progressive lung disease that includes conditions like emphysema and chronic bronchitis. When a chest infection aggravates COPD, the symptoms can worsen significantly.
Impact on Health:
- Worsened Breathing: Exacerbations of COPD can lead to significant increases in shortness of breath, coughing, and mucus production.
- Hospitalization Risk: People with COPD who develop chest infections are at a higher risk of requiring hospitalization due to severe respiratory distress.
- Long-Term Decline in Lung Function: Repeated chest infections can accelerate the decline of lung function in individuals with COPD, leading to more severe symptoms and a reduced quality of life.
5. Respiratory Failure
Respiratory failure is a severe complication that can arise from a chest infection, particularly if pneumonia or ARDS develops. Respiratory failure occurs when the lungs are unable to supply enough oxygen to the body or remove enough carbon dioxide, leading to life-threatening consequences.
Impact on Health:
- Life-Threatening: Respiratory failure requires immediate medical intervention, often involving mechanical ventilation or oxygen therapy to help the patient breathe.
- Organ Damage: Prolonged respiratory failure can lead to organ damage, particularly in the heart and kidneys, as they are deprived of the oxygen necessary for proper functioning.
- Rehabilitation Needs: Recovery from respiratory failure may involve a long stay in the intensive care unit (ICU), followed by extended rehabilitation to regain full lung function.
6. Heart Complications
Chest infections, particularly pneumonia, can also strain the heart. When the lungs are infected, the body’s oxygen levels drop, and the heart has to work harder to pump oxygenated blood throughout the body. In severe cases, chest infections can contribute to heart complications.
Impact on Health:
- Heart Failure: In patients with pre-existing heart conditions, chest infections can worsen heart failure symptoms, potentially leading to a heart attack or other cardiovascular events.
- Increased Risk of Arrhythmias: The stress caused by a chest infection can trigger irregular heart rhythms, which can be dangerous if not treated promptly.
- Long-Term Heart Damage: Prolonged low oxygen levels can lead to chronic strain on the heart, which may result in long-term heart damage.
7. Exacerbation of Existing Health Conditions
Individuals with underlying health conditions such as asthma, diabetes, or weakened immune systems are at an increased risk of complications from chest infections. For example, asthma can worsen significantly during a chest infection, leading to asthma attacks and increased difficulty breathing.
Impact on Health:
- Worsened Symptoms: Pre-existing conditions like asthma, diabetes, and autoimmune diseases can be exacerbated by chest infections, leading to a more complicated recovery process.
- Increased Risk of Severe Complications: People with compromised immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or with HIV/AIDS, may have a reduced ability to fight off infections, increasing the risk of severe complications like pneumonia and sepsis.
Preventing Chest Infection Complications
Preventing complications from chest infections begins with early recognition and treatment. Here are a few tips to reduce the risk of complications:
- Vaccination: Vaccines for influenza and pneumonia (such as the pneumococcal vaccine) can reduce the risk of infections and their complications.
- Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing and avoiding contact with sick individuals can help prevent the spread of respiratory infections.
- Prompt Medical Attention: Seek medical help as soon as symptoms of a chest infection appear, particularly if they worsen or do not improve with over-the-counter treatments.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: If you have a chronic respiratory condition, work closely with your healthcare provider to manage it effectively, reducing the risk of exacerbations.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking weakens the immune system and damages the lungs, increasing the likelihood of developing severe infections.
Conclusion
Chest infections are common, but they can have significant and sometimes life-threatening complications if not properly managed. From pneumonia and ARDS to heart issues and exacerbation of chronic conditions, the complications of chest infections can affect every part of the body. Early intervention, good hygiene, and vaccination can help prevent many of these complications. If you or a loved one experiences symptoms of a chest infection, it's important to seek medical care to reduce the risk of long-term health issues.


























0 comments: